const calcOnlyBoss = function (m) {
//获取可通过的周围四个点
function getChild({ x, y }) {
return [[x + 1, y], [x - 1, y], [x, y + 1], [x, y - 1]].filter(([x, y]) => { return (x < size && y < size && x >= 0 && y >= 0 && !(x == end.x && y == end.y)) }).map(([X, Y]) => flat.find(({ x, y }) => x == X && y == Y))
}
//尝试通路
function applyChild(parent) {
const child = getChild(parent)
const newChild = child.filter(c => {
const newCost = c.cost + parent.totalCost //子点总消耗=子点消耗+父点总消耗,只取总消耗最少的点作为最终路径点
const newLength = 1 + parent.totalLength //子点总步长=1+父点总步长,总消耗相同时只取总步长最少的点作为最终路径点
if (c.parent.size == 0) {
c.parent.add(parent)
c.totalCost = newCost
c.totalLength = newLength
} else if (c.parent.has(parent) && newCost >= c.totalCost) {
return false //终止走回路
} else {
if (c.totalCost == newCost) {
if (c.totalLength > newLength) {
c.totalLegnth = newLength
c.parent = new Set([parent])
} else if (c.totalLength == newLength) {
c.parent.add(parent)
} else {
return false
}
} else if (c.totalCost > newCost) {
c.totalCost = newCost
c.totalLength = newLength
c.parent = new Set([parent])
} else {
return false //终止消耗过高
}
}
return true
})
return newChild
}
//回溯路径 结果逆推顺序
function getRoute({ x, y, value, parent }, result) {
parent = [...parent].filter(({ x, y }) => !result.find(({ x: X, y: Y }) => x == X && y == Y))//不走回路
if (!(start.x == x && start.y == y)) {
result.push({ x, y, value })
parent.forEach(_parent => getRoute(_parent, [...result]))
} else {
routes.push(result)
}
}
function getPoint({ x, y, value }) {
return { x, y, value }
}
let startTime = Date.now()
let size = m.length;
let record = m.map((i, y) => i.map((m, x) => ({ x: x, y: y, value: m, cost: (m == 2) * 1, totalCost: 0, totalLength: 0, parent: new Set() })));
let flat = record.flat();
let start = flat.find(i => i.value == 1);
let end = flat.find(i => i.value > 3); //4为BOSS 5为楼梯
let result = applyChild(start);
let times = 1
//循环遍历通路
while (result.length > 0) {
result = result.map(c => applyChild(c)).flat()
times++
}
console.log(`直奔BOSS 遍历路径计算完毕 花费${Date.now() - startTime}ms 长度${size} 循环计算${times}次`)
//遍历结果
result = getChild(end).sort((a, b) => a.totalCost - b.totalCost)
result = result.filter(i => i.totalCost == result[0].totalCost)
let routes = []
result.forEach(i => { getRoute(i, [getPoint(end)]) })
//最终结果,[步数,战斗次数,宝箱数,正序路径]
routes = routes.map(i => ({ length: i.length, battle: i.filter(i => i.value == 2).length, chest: i.filter(i => i.value == 3).length, route: i.reverse() }))
//排序战斗次数优先、其次步数
routes.sort((a, b) => a.length - b.length).sort((a, b) => a.battle - b.battle)
console.log(`直奔BOSS 回溯路径计算完毕 花费${Date.now() - startTime}ms 长度${size} 循环计算${times}次`)
//返回最优结果
return routes[0]
}
之前算法有漏洞,只考虑了消耗,没考虑距离(步长),
在地图较大的时候,到终点的消耗最少的不同走法会有几十万到几百万种,之前的算法会将全部回溯记录下来然后再排序取最优解,这就导致了回溯循环计算量非常大,经常需要花费几十秒甚至直接会卡死、内存溢出
因此作为改进,在遍历的同时加入距离(步长)计算,消耗优先,距离其次,即在消耗最低的情况下取消耗较低的点作为最终路径点,在消耗相同时取距离最低的点作为最终路径点,这样在回溯的时候只会取最优解了,直接把冗余解全部剔除了,不会再卡死了
这是之前的算法的结果,9×9的遍历只要0~2ms,而回溯却要10000~30000ms,这肯定不正常
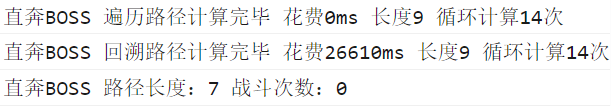
这是改进后的算法,10×10的遍历只要0~3ms,而回溯只要0~2ms