前文
跟一之哥有了那个想法
被毒打之后
个人还是有一点不服
于是决定开始尝试CDP协议的分析和学习
原理介绍
Chrome的调试和开发者工具实际是分离的
chrome内部起一个webscoket服务器
如果是使用Chrome内置的开发者工具
并不会使用Webscoket
而是使用chrome内部的全局函数进行通信
但是其大致原理是不变的
我们可以将chrome内部的服务器称之为backed
而将vscode或者f12等进行调试的称之为fronted
通信的协议称之为CDP协议
而诸如Websocket,或全局函数称之为通信的媒介
以上来自于神光大佬的前端调试通关秘籍
网址https://s.juejin.cn/ds/kuLGA1b/
大家有兴趣也可以买一本
实践
那我们可以开始尝试一下,首先创建一个快捷方式,在末尾加上
--remote-debugging-port=9222
然后启动
注意这里,启动之前必须打开任务管理器确保没有chrome
有时候可能挂在后台进程,导致启动合并而没有打开端口
接下来我们尝试一下链接
这里我用的ws库
var WebSocketClient = require("ws");
const chromePort = 9222;
var chromeSocket = new WebSocketClient("ws://localhost:" + chromePort);
发现失败了
为什么?
我们可以看一个已经完成的实现【chrome-remote-interface】
他的使用方式还是挺简单的,我们看一下demo
async function example() {
let client;
try {
// connect to endpoint
client = await CDP();
// extract domains
const { Network, Page } = client;
// setup handlers
// enable events then start!
await Network.enable();
await Page.enable();
await Page.navigate({ url: "https://github.com" });
await Page.loadEventFired();
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
} finally {
if (client) {
await client.close();
}
}
}
example();
那我们就去看看CDP源码
function CDP(options, callback) {
if (typeof options === 'function') {
callback = options;
options = undefined;
}
const notifier = new EventEmitter();
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
// allow to register the error callback later
process.nextTick(() => {
new Chrome(options, notifier);
});
return notifier.once('connect', callback);
} else {
return new Promise((fulfill, reject) => {
notifier.once('connect', fulfill);
notifier.once('error', reject);
new Chrome(options, notifier);
});
}
}
可以发现默认应该是调用了new Chrome
我们继续往里看
class Chrome extends EventEmitter {
constructor(options, notifier) {
super();
// options
const defaultTarget = (targets) => {
// prefer type = 'page' inspectable targets as they represents
// browser tabs (fall back to the first inspectable target
// otherwise)
let backup;
let target = targets.find((target) => {
if (target.webSocketDebuggerUrl) {
backup = backup || target;
return target.type === 'page';
} else {
return false;
}
});
target = target || backup;
if (target) {
return target;
} else {
throw new Error('No inspectable targets');
}
};
options = options || {};
this.host = options.host || defaults.HOST;
this.port = options.port || defaults.PORT;
this.secure = !!(options.secure);
this.useHostName = !!(options.useHostName);
this.alterPath = options.alterPath || ((path) => path);
this.protocol = options.protocol;
this.local = !!(options.local);
this.target = options.target || defaultTarget;
// locals
this._notifier = notifier;
this._callbacks = {};
this._nextCommandId = 1;
// properties
this.webSocketUrl = undefined;
// operations
this._start();
}
}
可以没什么操作,调用了_start()
我们继续往里看
async _start() {
const options = {
host: this.host,
port: this.port,
secure: this.secure,
useHostName: this.useHostName,
alterPath: this.alterPath
};
try {
// fetch the WebSocket debugger URL
const url = await this._fetchDebuggerURL(options);
// allow the user to alter the URL
const urlObject = parseUrl(url);
urlObject.pathname = options.alterPath(urlObject.pathname);
this.webSocketUrl = formatUrl(urlObject);
// update the connection parameters using the debugging URL
options.host = urlObject.hostname;
options.port = urlObject.port || options.port;
// fetch the protocol and prepare the API
const protocol = await this._fetchProtocol(options);
api.prepare(this, protocol);
// finally connect to the WebSocket
await this._connectToWebSocket();
// since the handler is executed synchronously, the emit() must be
// performed in the next tick so that uncaught errors in the client code
// are not intercepted by the Promise mechanism and therefore reported
// via the 'error' event
process.nextTick(() => {
this._notifier.emit('connect', this);
});
} catch (err) {
this._notifier.emit('error', err);
}
}
发现这里进行了Websocket的链接
await this._connectToWebSocket();
追一下发现他直接进行了链接,传入的是webSocketUrl
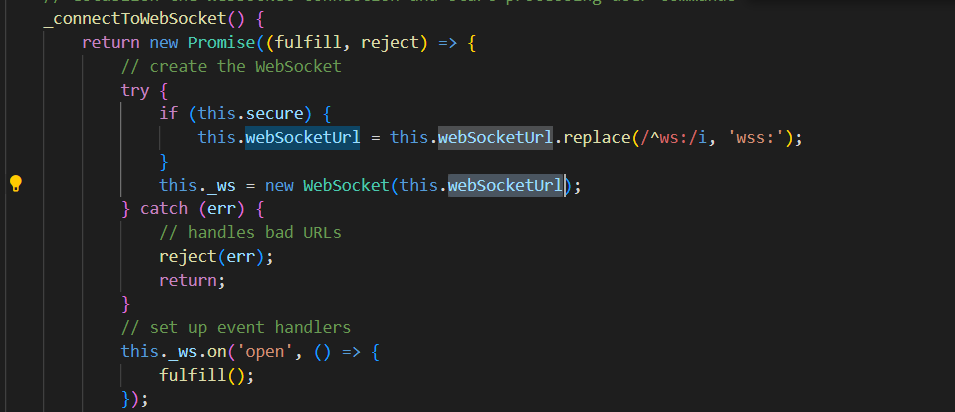
我们可以发现他用的也是ws库,那基本可能就是webSocketUrl的问题了
我们看一下他的webSocketUrl哪里来的
搜一下找到了_start里
// fetch the WebSocket debugger URL
const url = await this._fetchDebuggerURL(options);
// allow the user to alter the URL
const urlObject = parseUrl(url);
urlObject.pathname = options.alterPath(urlObject.pathname);
this.webSocketUrl = formatUrl(urlObject);
看一下fetchDebuggerURL里
// fetch the WebSocket URL according to 'target'
async _fetchDebuggerURL(options) {
const userTarget = this.target;
switch (typeof userTarget) {
case 'string': {
let idOrUrl = userTarget;
// use default host and port if omitted (and a relative URL is specified)
if (idOrUrl.startsWith('/')) {
idOrUrl = `ws://${this.host}:${this.port}${idOrUrl}`;
}
// a WebSocket URL is specified by the user (e.g., node-inspector)
if (idOrUrl.match(/^wss?:/i)) {
return idOrUrl; // done!
}
// a target id is specified by the user
else {
const targets = await devtools.List(options);
const object = targets.find((target) => target.id === idOrUrl);
return object.webSocketDebuggerUrl;
}
}
case 'object': {
const object = userTarget;
return object.webSocketDebuggerUrl;
}
case 'function': {
const func = userTarget;
const targets = await devtools.List(options);
const result = func(targets);
const object = typeof result === 'number' ? targets[result] : result;
return object.webSocketDebuggerUrl;
}
default:
throw new Error(`Invalid target argument "${this.target}"`);
}
}
根据userTarget判断不同类型,他来自于this.target;
如果不给任何参数,默认来自于
const defaultTarget = (targets) => {
// prefer type = 'page' inspectable targets as they represents
// browser tabs (fall back to the first inspectable target
// otherwise)
let backup;
let target = targets.find((target) => {
if (target.webSocketDebuggerUrl) {
backup = backup || target;
return target.type === 'page';
} else {
return false;
}
});
target = target || backup;
if (target) {
return target;
} else {
throw new Error('No inspectable targets');
}
};
相当于获取所有targets,看代码来说基本是获取第一个存在webSocketDebuggerUrl,并且type为page的,那targets哪里来的?
我们找到devtools.List(options)里,发现了
function List(options, callback) {
devToolsInterface('/json/list', options, (err, tabs) => {
if (err) {
callback(err);
} else {
callback(null, JSON.parse(tabs));
}
});
}
devToolsInterface类似于直接访问网页
我们直接访问http://127.0.0.1:9222/json/list
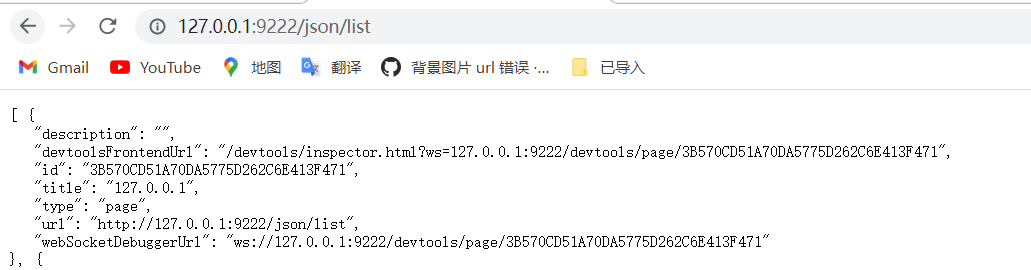
就找到了socket的地址,那我们自己实现一下
var WebSocketClient = require("ws").WebSocket;
var axios = require("axios");
const chromePort = 9222;
function getWebscoketUrl() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
axios
.get("http://127.0.0.1:" + chromePort + "/json/list")
.then((response) => {
const target = response.data.find((item) => {
return (
item.webSocketDebuggerUrl !== undefined && item.type === "page"
);
});
resolve(target.webSocketDebuggerUrl);
});
});
}
async function main() {
const getWebsocketUrl= await getWebscoketUrl();
var chromeSocket = new WebSocketClient(getWebsocketUrl);
chromeSocket.onopen = function (e) {
console.log("Connection to server opened");
};
}
main();
测试发现正常提示了Connection to server opened
那我们就完成了对CDP的连结
结语
撒花~